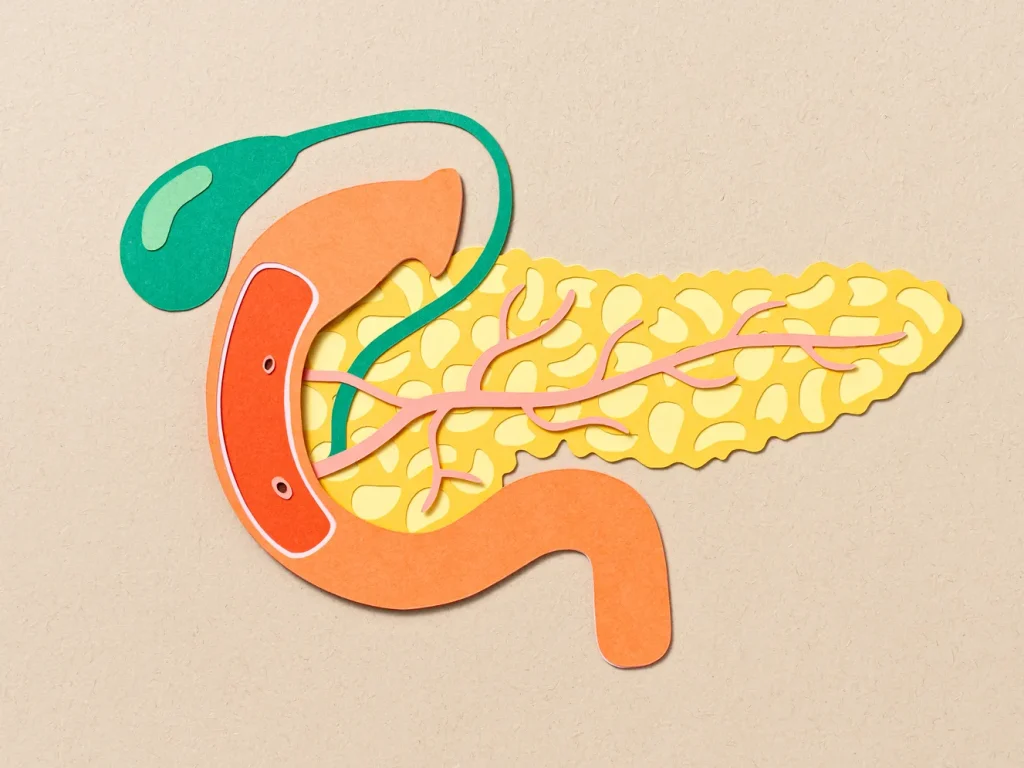
Understanding Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the digestive system, which includes the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas and gallbladder. Gastroenterologists are specialists who diagnose and treat various gastrointestinal disorders such as acid reflux, ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease and hepatitis.
Common Conditions Treated
One of the most common conditions treated in this area is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). GERD can cause chronic heartburn and discomfort and often requires lifestyle changes and medications to manage effectively. It is essential that GERD is addressed promptly to prevent complications such as esophageal damage.
The Impact of IBD
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, are chronic conditions that cause inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. These diseases require careful management with anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants and sometimes surgery. Effective treatment helps prevent complications and improves the quality of life of those affected.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Gastroenterology relies on a variety of diagnostic tools to accurately identify and monitor conditions. Endoscopy is a common procedure that allows specialists to examine the digestive tract using a flexible tube with a camera. Colonoscopy, a type of endoscopy, is particularly important for screening and diagnosing problems in the colon and rectum.

Advancements in technology have greatly improved the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. Capsule endoscopy, for example, involves swallowing a small, pill-sized camera that takes detailed images of the digestive tract.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Each patient is unique, so personalized treatment plans are essential. These plans are based on individual symptoms, medical history and lifestyle. They usually include a combination of medications, lifestyle changes and regular monitoring to achieve the best results.
Importance of Diet and Nutrition
Diet plays an important role in the management of gastrointestinal disorders. For example, GERD patients are advised to avoid trigger foods, eat smaller meals and elevate the head of their bed. Those with IBS can benefit from a low FODMAP diet, which involves avoiding certain carbohydrates that can trigger symptoms.
Patient Education and Support
In gastroenterology, it is essential to educate patients about their conditions and how to manage them. Understanding the nature of their condition, the importance of adherence to treatment and the role of lifestyle changes empowers patients to take control of their health.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate gastrointestinal symptoms, so managing stress is crucial. In a bustling city like Dubai, it can be easy to feel overwhelmed. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation and deep breathing exercises help many patients stay calm and centered, which helps them manage their symptoms more effectively.
Professional Reflections
on Gastroenterology
Working in gastroenterology is incredibly rewarding. Seeing patients improve their health and quality of life through effective management and treatment is what motivates me. The field is constantly evolving with new research and advances, making it an exciting and dynamic area of medicine.

Articles
The Dangers of Ignoring Rectal Bleeding
Have you ever noticed a small streak of blood and tried to convince yourself that it was nothing worth attention during a busy day? Many people face this moment and[…]
Read morePreventing and Treating Painful Stomach Ulcers
Have you ever wondered why a simple burning feeling can grow into days of discomfort despite your routine staying the same? Many readers describe the first signs as a mild[…]
Read moreGas and Bloating After Meals: What’s the Cause?
Gas and bloating after meals can feel confusing and uncomfortable, and recognizing the simple reasons behind these symptoms may help you understand your body better during daily routines. Why does[…]
Read moreBloating: When It’s Normal and When It’s Not
Have you ever finished a meal and felt your waistband tighten uncomfortably within an hour. Maybe you wondered if it was just a heavy lunch or something more serious hiding[…]
Read moreHow to Manage Chronic Constipation Effectively
Chronic constipation is not a singular ailment but a spectrum of conditions unified by infrequent bowel movements or the difficult passage of stool, a state persisting over several months. It[…]
Read moreHow to Maintain a Strong and Healthy Gut Daily
The pursuit of daily well-being often overlooks a crucial and complex internal system: the gut. Far from being a mere conduit for food passage, the gastrointestinal tract operates as a[…]
Read moreIs Your Diet Causing Bloating and How to Fix It?
The persistent, uncomfortable sensation of abdominal bloating—often described as a tight, swollen, or painfully distended feeling—is a profoundly frustrating experience that often serves as a direct, undeniable signal that the[…]
Read moreThe Gut – Brain Axis: What You Should Know
The connection between the gastrointestinal tract and the central nervous system has moved decisively from anecdotal observation—the familiar “gut feeling”—to a cornerstone of modern neurobiology and gastroenterology. The Gut-Brain Axis[…]
Read moreTop Questions to Ask Your Gastroenterologist
The visit to a Gastroenterologist (GI) often comes at a moment of significant uncertainty or discomfort, dealing with symptoms that are frequently complex, pervasive, and deeply personal. Effectively leveraging the[…]
Read more